This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of obtaining a food and beverage license in Nepal, from understanding what it is to the benefits it offers your business.
What is a Food and Beverage License in Nepal?
A food and beverage license in Nepal is an official permit issued by the government that allows businesses to legally operate in the food and drink industry. This license serves as proof that your establishment meets the necessary health, safety, and quality standards set by Nepali authorities.
Which Authority Issues Food and Beverage Licenses?
The Department of Food Technology and Quality Control (DFTQC) is the primary authority responsible for issuing food and beverage licenses in Nepal. This department operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development.
The DFTQC has several key responsibilities:
- Issuing food and beverage licenses
- Conducting inspections of food establishments
- Enforcing food safety standards
- Monitoring food quality across the country
- Providing guidance on food regulations
Municipality/Village Municipality also play a role in the licensing process, often working in coordination with the DFTQC.
What is the Process for Obtaining Food License in Nepal?
Step 1: Business Registration (Company or Gharelu)
Step 2: Local Ward & Tax Registration
Step 3: Registration at Department of Food, Technology and Quality Control
Step 4: Testing of Products at DFTQC
Step 5: Verification of Products
Step 6: Obtain Food and Beverage License
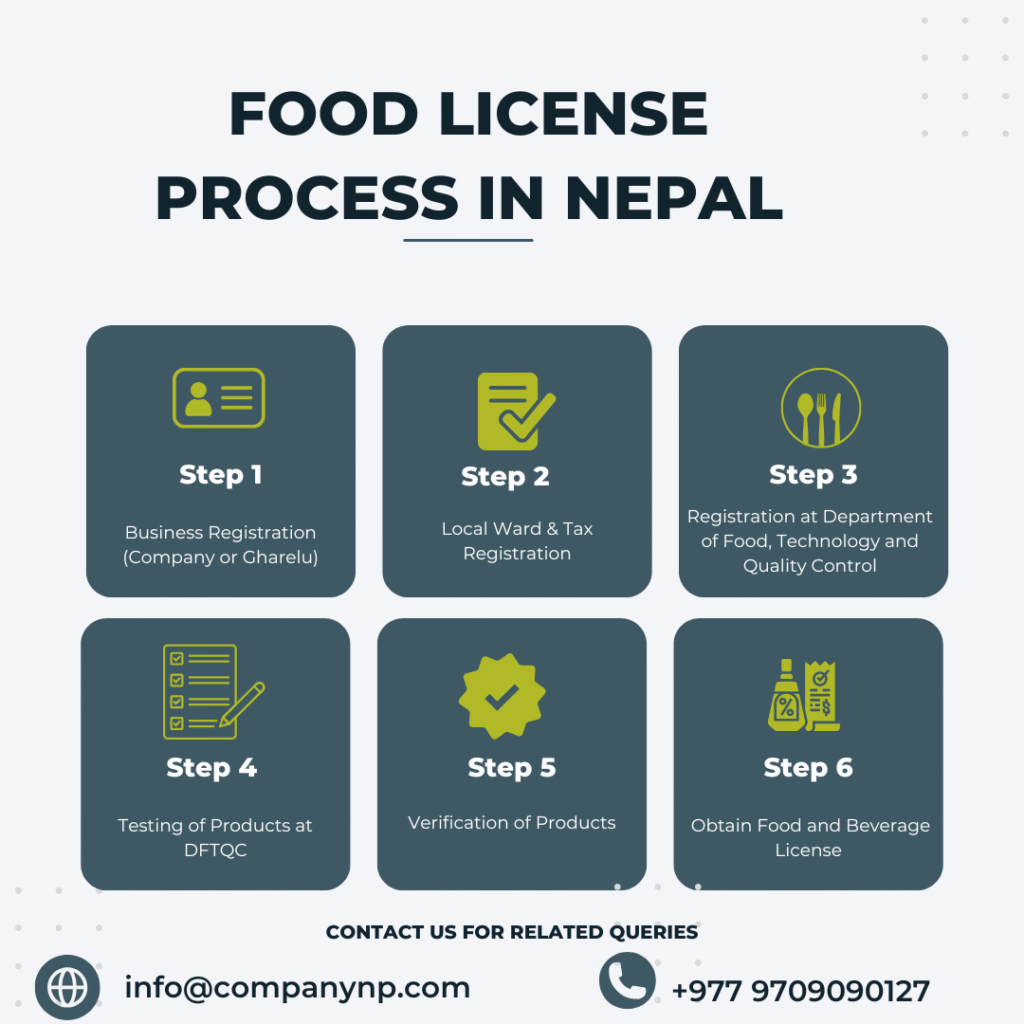
Step 1: Business Registration (Company or Gharelu)
First, the Food/Beverage Business must be registered with the Office of Company Registrar or the Department of Small Industries. Consult us if you are confused on the type of business to be registered.
Step 2: Local Ward & Tax Registration
After successful registration of the business, they must be respectively registered at the Tax Office and the Ward Office.
Step 3: Registration at Department of Food, Technology and Quality Control
Thereafter, the Business must be registered at DFTQC. To register the business, it must provide all the certificates of Registration along with the necesary infrastructure for the preparation of the Food/Beverage.
Step 4: Testing of Products at DFTQC
The Department conducts tests and reviews the food/beverage.
Step 5: Verification of Products
The Department provides further verification after the product has been successfully verified and ready for production.
Step 6: Obtain Food and Beverage License
Thereafter, you can mass-produce, scale and launch the product through the License.
Note: The License is for a specific product only and not the Whole Company. New Products must be simultaneously registered.
Documents required for Food/Beverage License in Nepal
When applying for a food and beverage license in Nepal, you’ll need to prepare and submit several documents. Here’s a list of the commonly required items:
- Completed application form
- Citizenship certificate of the business owner
- Business registration certificate
- PAN (Permanent Account Number) certificate
- Tax clearance certificate
- Rental agreement or proof of property ownership
- Building permit (for permanent structures)
- Health certificates for staff members
- Food handler training certificates
- Menu or product list (for restaurants and food manufacturers)
- Label designs (for packaged food products)
- Water quality test report
Note that additional documents may be required depending on the nature of your business and local regulations. It’s advisable to check with the DFTQC for the most current list of required documents.
How Long Does the Licensing Process Take?
The duration of the food and beverage licensing process in Nepal can vary depending on several factors:
Factors Affecting Processing Time
- Completeness of your application
- Workload of the DFTQC
- Type and complexity of your food business
- Results of the inspection
- Any required follow-up actions
Typical Timeline
On average, the process can take anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks. Here’s a rough breakdown:
- Application submission and initial review: 1-2 weeks
- Scheduling and conducting inspection: 1-3 weeks
- Evaluation and decision-making: 1-2 weeks
- License issuance (if approved): 1 week
To ensure a smooth process, submit a complete application with all required documents. Promptly respond to any requests for additional information or clarification from the DFTQC.
What are the Costs of Obtaining the License?
The costs associated with obtaining a food and beverage license in Nepal can be broken down into several categories:
Official Fees
- Application fee: NPR 1,000 – 5,000 (varies based on business type)
- License fee: NPR 2,000 – 10,000 (depends on business size and type)
- Inspection fee: NPR 1,000 – 3,000
Additional Costs
- Document preparation: NPR 2,000 – 5,000 (if using a service)
- Health certificates for staff: NPR 500 – 1,000 per person
- Food handler training: NPR 1,000 – 3,000 per person
- Water quality testing: NPR 2,000 – 5,000
Potential Indirect Costs
- Upgrades to meet safety standards: Varies widely
- Legal or consulting fees: NPR 5,000 – 20,000
Note that these are approximate costs and may vary. Always check with the DFTQC for the most current fee structure.
What are Post-License Requirements for Businesses?
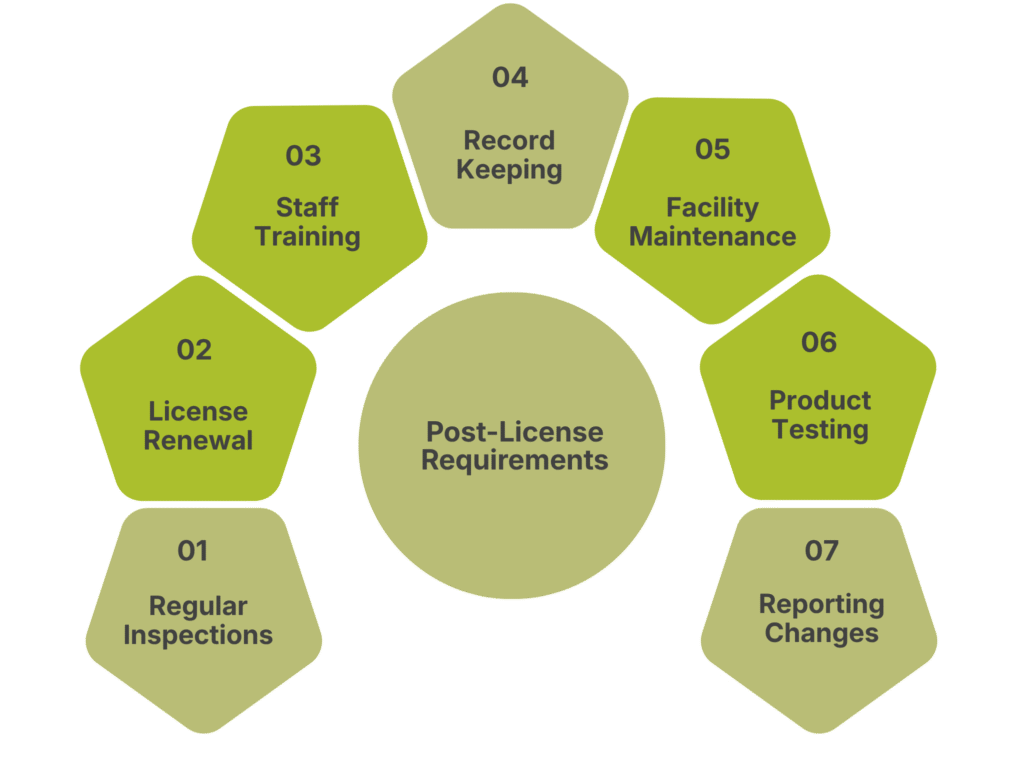
After obtaining your food and beverage license in Nepal, there are ongoing requirements to maintain compliance:
1. Regular Inspections
Be prepared for periodic inspections by DFTQC officials to ensure continued compliance with food safety standards.
2. License Renewal
Licenses typically need to be renewed annually. Start the renewal process at least a month before expiration.
3. Staff Training
Regularly train your staff on food safety practices and keep their certifications up to date.
4. Record Keeping
Maintain detailed records of food sourcing, preparation processes, and any customer complaints or incidents.
5. Facility Maintenance
Keep your premises clean and well-maintained, adhering to the standards set during your initial licensing.
6. Product Testing
For food manufacturers, conduct regular product testing to ensure quality and safety.
7. Reporting Changes
Inform the DFTQC of any significant changes to your business, such as new menu items or changes in ownership.
What Types of Food and Beverage Licenses Exist?
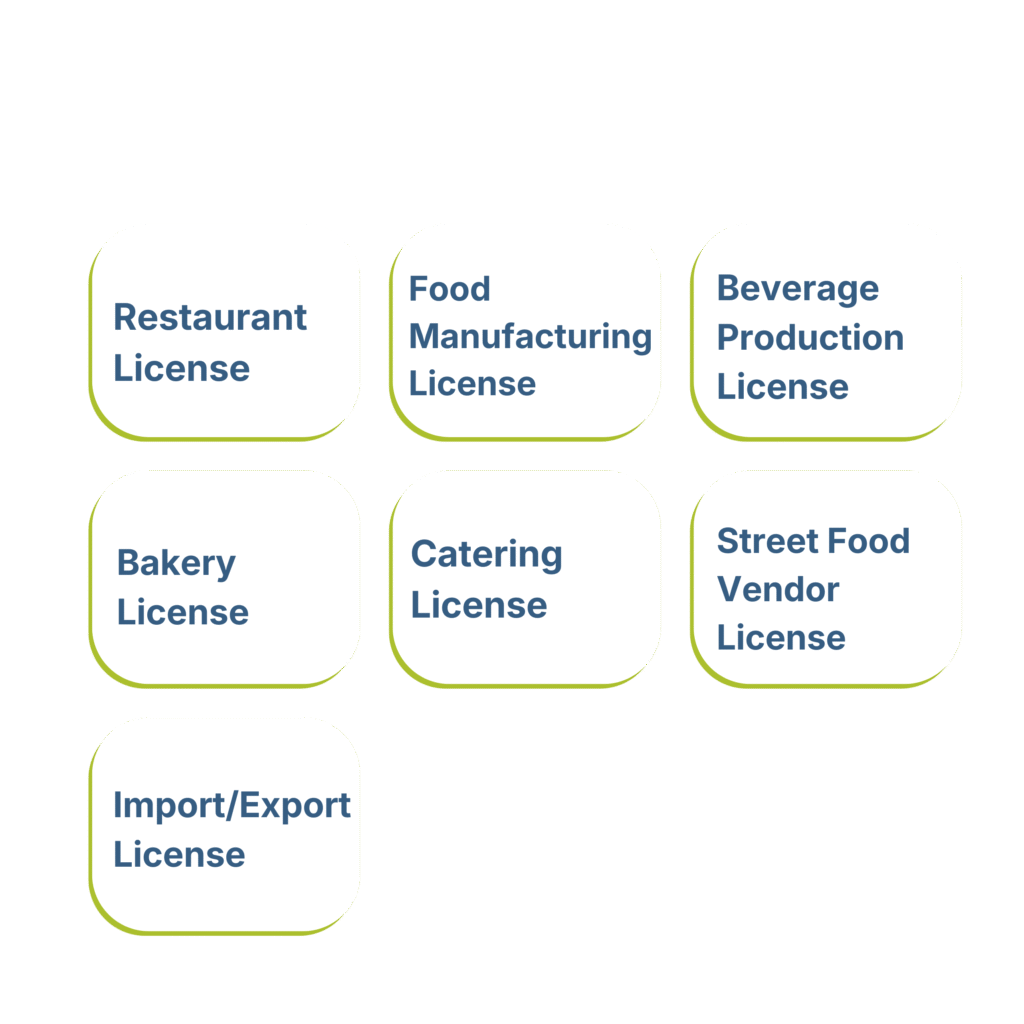
Nepal offers various types of food and beverage licenses to accommodate different business models:
1. Restaurant License
For businesses primarily serving prepared meals to customers on-site.
2. Food Manufacturing License
For businesses producing packaged food products for retail or wholesale.
3. Beverage Production License
Specifically for businesses producing drinks, both alcoholic and non-alcoholic.
4. Bakery License
For businesses specializing in baked goods and confectioneries.
5. Catering License
For businesses providing food services at events or other locations.
6. Street Food Vendor License
A specialized license for mobile food vendors and street food stalls.
7. Import/Export License
For businesses involved in international food trade.
What Laws Govern Food and Beverage Licensing?
Several laws and regulations govern food and beverage licensing in Nepal. Understanding these legal frameworks is essential for businesses operating in the industry:
1. Food Act, 2023 (1966)
This is the primary legislation governing food safety and quality in Nepal. It outlines the basic requirements for food businesses and sets penalties for violations.
2. Food Rules, 2027 (1970)
These rules provide more detailed guidelines on implementing the Food Act, including specific requirements for different types of food businesses.
3. Food Regulation Directives, 2075 (2018)
This directive outlines the latest standards and procedures for food safety management, including licensing requirements.
4. Local Government Operation Act, 2074 (2017)
This act gives local governments some authority in regulating food businesses within their jurisdictions.
5. Consumer Protection Act, 2075 (2018)
While not specifically about food licensing, this act influences food businesses by setting standards for consumer rights and product quality.
The specific requirements and processes may vary slightly for each license type, so be sure to clarify which category your business falls under when applying.
Read More:
Construction Permit Process in Nepal
Trademark Registration Process in Nepal
Automobile Company Registration in Nepal
What are the Benefits of Having a License?
Obtaining a food and beverage license in Nepal offers numerous advantages for your business:
- Legal Compliance: Operate your business legally, avoiding fines or closure.
- Consumer Trust: Licensed businesses are viewed as more trustworthy by customers.
- Quality Assurance: The licensing process ensures your business meets quality standards.
- Access to Support: Licensed businesses can access government resources and support.
- Competitive Advantage: Stand out from unlicensed competitors in the market.
- Easier Expansion: A valid license makes it easier to expand your business or seek funding.
- Protection from Liability: Compliance with standards can help protect your business from legal issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need Food/Beverage License in Nepal?
Yes, a Business requires a Food/Beverage License issued by DFQTC (खाद्य विभाग) to manafucture and sell food/beverage products. To determine whether you need the License or not, request a consultation.
What is the process of Food/Beverage License in Nepal?
Step 1: Business Registration (Company or Gharelu)
Step 2: Local Ward & Tax Registration
Step 3: Registration at Department of Food, Technology and Quality Control
Step 4: Testing of Products at DFTQC
Step 5: Verification of Products
Step 6: Obtain Food and Beverage License
How to register Food License in Nepal?
Register Food/Beverage Products to follow them:
1. Complete Business Registration
2. Send an Application to DFQTC
3. Obtain Approval from DFTQC
4. Testing and Verification of Products
5. Successful Availability of Food and Beverage License
What is a Food and Beverage License in Nepal?
It is an approval issued by the Department of Food Technology and Quality Control (DFTQC) allowing businesses to produce, process, or sell food and beverage products legally.
What documents are required for the license?
Basic documents include company/firm registration, PAN/VAT, owner’s ID, location map, product details, hygiene plan, and lab test reports if applicable.
Consult an Expert
Refer the Following:
Business Permits and License in Nepal
Microbreweries License in Nepal
Contents
- 1 What is a Food and Beverage License in Nepal?
- 2 Which Authority Issues Food and Beverage Licenses?
- 3 What is the Process for Obtaining Food License in Nepal?
- 4 Documents required for Food/Beverage License in Nepal
- 5 How Long Does the Licensing Process Take?
- 6 What are the Costs of Obtaining the License?
- 7 What are Post-License Requirements for Businesses?
- 8 What Types of Food and Beverage Licenses Exist?
- 9 What Laws Govern Food and Beverage Licensing?
- 10 What are the Benefits of Having a License?









